
Dr Kirollos Hanna details clinical trial data on the use of zanubrutinib in treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

Dr Kirollos Hanna details clinical trial data on the use of zanubrutinib in treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia.

Lisa Nodzon, PhD, ARNP, AOCNP, and Javier Pinilla-Ibarz, MD, PhD, review challenges in CLL therapy, including cost barriers.

Further, the 1-year update suggests that Cohort 6 toxicity management strategy can improve certain AEs without compromising the activity of axicabtagene ciloleucel.

Umbralisib (Ukoniq) is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma and relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.
The research team conducted a systematic review to collect the available published evidence on the topic and then combined the results using a process called meta-analysis.
Javier Pinilla-Ibarz, MD, PhD; Lisa Nodzon, PhD, ARNP, AOCNP; and Katie Tobon, PharmD, BCOP, describe the incidence of CLL and discuss factors that may increase the risk of disease.

Kovaltry temporarily replaces the missing clotting Factor VIII in patients with hemophilia A.

IMX-110 is a tissue-specific therapeutic designed to accumulate at intended therapeutic sites at 3 to 5 times the rate of conventional therapeutics.
The observed increase in patient age at the time of relapse makes the findings even more impressive because longer survival is typically associated with younger age at the time of relapse.

C-CAR039 showed positive efficacy and safety data in patients with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Giant cell arteritis frequently causes headaches, scalp tenderness, jaw pain and vision problems.

Emicizumab (Hemlibra, Roche) is indicated for routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce the frequency of bleeding episodes in adults and children with hemophilia A with or without factor VIII inhibitors.
The submission is supported by data from MajesTEC-1, a multicenter clinical trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of teclistamab in adults with RRMM.
The metabolic protein SIRT3 reduces the pools of amino acids that cells use to make proteins and otherwise fuel their growth.
Rivaroxaban is indicated to reduce the risk of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation, for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism.

Crestor is indicated for the treatment of patients with primary hyperlipidemia and mixed dyslipidemia.

Abatacept is also approved for adults with moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis, active psoriatic arthritis, and moderate to severe polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis for children 2 years of age and older.

The treatment was first approved in 2013 for adults as a 1500 mg course of treatment, administered as 2 doses of 750 mg each separated by at least 7 days.

Study may help guide COVID-19 vaccination strategies for patients with blood disorders.
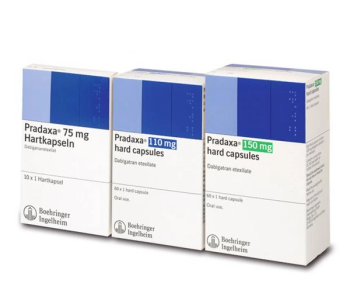
Dabigatran and its acyl glucuronides are competitive, direct thrombin inhibitors.

This trial is the first to assess the use of isatuximab as a first-line treatment for newly diagnosed, transplant-eligible patients up to 70 years of age, according to the study authors.
However, active disease alone for hospitalized patients was not associated with greater odds of dying from COVID-19, nor was receiving ongoing cancer treatment.

Data from a couple of new molecules could be encouraging for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma

In addition to data showing the durable efficacy of acalabrutinib, other data presented at ASH 2021 demonstrate that the new tablet formulation of the drug supports ease of use for patients
Emicizumab-kxwh demonstrated a favorable safety profile and effective bleed control in people with mild or moderate hemophilia A without factor VIII inhibitors.