Cholesterol
Latest News
Latest Videos

Shorts
Podcasts
CME Content
More News
Lerodalcibep, a new PCSK9 inhibitor, offers a convenient monthly injection to effectively lower LDL cholesterol in patients with hypercholesterolemia.

New research reveals that low cholesterol levels may indicate increased severity in Crohn disease, offering a potential new biomarker for monitoring inflammation.

Implementing a best practice advisory into physicians’ electronic health records improved lipid therapy initiation and diagnoses of hyperlipidemia and hypercholesterolemia.
A more significant association with cardiovascular disease (CVD) was observed among individuals with diabetes compared with those without.
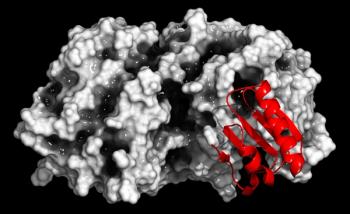
The investigational, oral PCSK9 inhibitor has the potential to significantly reduce low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in patients with hypercholesterolemia or patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
Young adults with high LDL-C levels face significant gaps in statin initiation and follow-up testing, highlighting urgent needs for improved cardiovascular care.

At 3 and 9 months, inclisiran reduced low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in patients intolerant to statins or proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors at rates comparable to those in placebo-controlled trials.
A genomic screening initiative identified patients harboring a familial hypercholesterolemia genetic variation and directed them toward LDL-C-lowering therapies, inducing meaningful reductions.

Survivors of ischemic stroke had a lower risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) when achieving low levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
Total cholesterol and triglyceride levels were linked to an increased risk of Alzheimer-related declines in cognitive function, whereas high-density lipoprotein cholesterol provided a protective effect.

A heightened ratio of non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C) to HDL-C was associated with depression, with risk mediated by body mass index.
An index of total cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL), and fasting glucose levels was found to indicate the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in a nationally representative US cohort.
The ratio of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) to low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) can predict cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in patients with and without diabetes.
A retrospective analysis found no associations between lipid parameters and the success of blood stem cell mobilization in a cohort of healthy donors.
The angiopoietin-like-3-targeting treatment received an expanded indication for individuals aged 1 through 5 years, building on earlier approvals in older populations.

New research reveals that eggs do not raise bad cholesterol; instead, saturated fat in the diet is the real culprit for heart disease.
Inclisiran, a small interfering RNA PCSK9 inhibitor, was effective and tolerable in real-world practice, though pharmacists must make important considerations for patients switching from another medicine.
A meta-analysis found that proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors induce sustained reductions across lipid biomarkers, including low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C).
Young, non-diabetic individuals were most likely to delay statin initiation for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) lowering, increasing their risk of myocardial infarction.
Participating in a pharmacist-led secondary intervention clinic helped achieve large reductions in cholesterol levels among patients who have experienced an acute coronary syndrome.
A series of PCSK9 inhibitors were found to be tolerable and effective at reducing low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in solid organ transplant recipients.
Recaticimab significantly lowered low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels, showing promise in becoming a future proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) option for cholesterol reduction.
In combination with lipid-lowering therapy, inclisiran allowed patients with hypercholesterolemia to reach their low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) goals without associated muscle-related adverse events.
A new oral PCSK9 inhibitor, enlicitide, shows promise in significantly lowering LDL cholesterol, offering hope for hypercholesterolemia management and cardiovascular health.
A retrospective analysis found widespread lack of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) goal attainment, posing risks for those at very high cardiovascular risk.