Lymphoma
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Lisocabtagene maraleucel chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy significantly enhances treatment of relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies, offering high response rates and durable remissions.
There were 2 main types of switches, including switching to rituximab subcutaneous and switching among different intravenous rituximab treatments.
Outpatient models are emerging as feasible alternatives to traditional inpatient care, offering potential benefits such as reduced hospitalization, improved social well-being, and cost savings.

The risk of developing lymphoma remained nearly the same between patients with Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis.
Comprising most cases of this rare form of lymphoma, it is essential that pharmacists and treatment providers are aware of the health-related burdens patients with these subtypes consistently face.
Compared with brentuximab vedotin and chemotherapy, nivolumab and chemotherapy had longer progression-free survival and a better safety profile.
The results indicate the potential use of loncastuximab tesirine as a treatment option for the rare hyperinflammatory condition.
CAR T-cell therapy on an outpatient basis could lead to greater adherence and less financial and physical burdens.
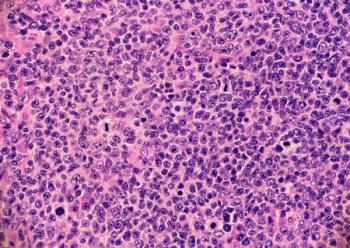
The results show promise for the use of Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors in non-Hodgkin lymphoma treatment.
Patients exhibited improved disease-free progression with minimal adverse effects.
Zanubrutinib demonstrated sustained responses in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL).
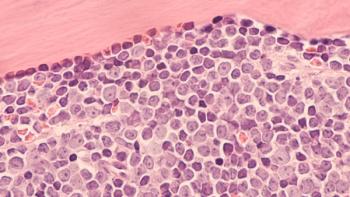
Poorer prognosis was linked to factors such as reduced hemoglobin levels and advanced stage at diagnosis.
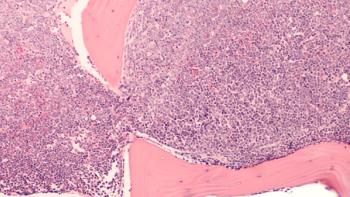
These results indicate the combination’s long-term effectiveness in a population with limited treatment options.
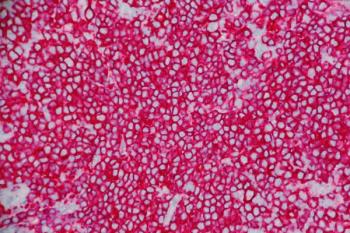
Improvements in survival outcomes were seen among those at high risk for DLBCL who received 6x R-CHOP21 + 2R.
Presenter Krish Patel, MD, discusses the use of epcoritamab (Epkinly; AbbVie) and glofitamab (Columvi; Genentech) in aggressive B-cell lymphomas as monotherapies and in combination regimens.
Experts debate over the most effective treatment pathway for Richter transformation, highlighting the risks and benefits of different cellular therapies.
Reid Merryman, MD, discusses the potential for minimal residual disease (MRD) to inform treatment decisions, identify lymphoma subgroups, and infer gene expression.
Surprisingly, those with overweight BMI at diagnosis did not have a poor prognosis.
Patients with DLBCL on Medicaid had worse survival outcomes than those on commercial insurance, but there were no statistically significant differences in survival between races.
In survivors of lymphoma with fragmented transition of care, preparedness and activation for the next phase of their survivorship was lacking.
The indication is for adults with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma who were treated with at least 2 prior lines of therapy.
Aligning with previous data, the drug combination was modestly effective in patients with large B-cell lymphoma pre- and post-CAR-T-cell therapy.

Bendamustine resulted in a greater risk of treatment complications in patients with lymphoma.
This article reviews the efficacy and safety data for bispecific T-cell engagers and the practical considerations for their implementation across various types of practice sites for the historically difficult-to-treat relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma population.
Building off the positive results of ELM-1, the ELM-2 trial found intravenously administered odronextamab was safe and effective in patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.