Lung Cancer
Latest News

From Diagnosis to Delivery: How Multidisciplinary Teams Tackle Stage 3A Lung Cancer
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
The therapy offers new hope in solid tumor treatment with fewer adverse effects.
HER2-mutant NSCLC is associated with poor prognosis. Zongertinib and BAY 2927088 are HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors that have activity in NSCLC with manageable toxicity profiles.

Shirish Gadgeel, MD, discusses an integrated analysis of the regional TRUST-I study and global TRUST-II study presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress 2024.

Shirish Gadgeel, MD, discusses the promising results of the randomized phase 3 HARMONi-2/AK112-303 study comparing ivonescimab to pembrolizumab in PD-L1–positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer.

Longer-term data from the phase 3 MARIPOSA trial confirm superior outcomes of a chemotherapy-free amivantamab-vmjw plus lazertinib regimen compared to osimertinib monotherapy as first-line therapy.

At the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer, Ana Baramidze, MD, PhD, presented 5-year outcomes of the trial, which investigated cemiplimab monotherapy in first-line advanced non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with PD-L1 expression of 50% or greater.

At the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer, Benjamin Besse, MD, PhD, discussed the findings of the phase 3 CARMEN-LCO3 trial, which led to the discontinuation of the study drug by the manufacturer.

Nivolumab is the only PD-1 inhibitor to show statistically significant and clinically meaningful benefits in non-small cell lung cancer compared with chemotherapy.
Currently, standard first-line chemotherapy with or without immunotherapy for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with HER2 mutations has limited efficacy.

The decision is based on positive results from the phase 3 LAURA trial.
Amivatamab-vmjw is a fully-human bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and MET with immune cell-directed activity.

The combination of amivantamab and lazertinib showed improved intracranial efficacy, progression-free survival, and overall survival for non-small cell lung cancer.
Abstracts from the OrigAMI-1 and MARIPOSA-2 trials indicated the treatment benefits of amivantamab-vmjw and chemotherapy in multiple cancer indications.
Clinical research presented at ESMO 2024 highlights the significant survival benefits of perioperative and neoadjuvant immunotherapy with nivolumab and nivolumab plus ipilimumab, while emphasizing the role of biomarkers such as ctDNA and KRAS mutations in guiding treatment decisions.
An ESMO 2024 presentation explores the growing role of the gut microbiome in immunotherapy response, emerging diagnostic tools such as PCR chips, and innovative therapies such as fecal microbiota transplantation and microbiome-preserving strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Christian Rolfo discusses 6 different treatment options that are being developed across immunotherapies and antibody drug conjugates for non–small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer.
Subcutaneous administration of atezolizumab and hyaluronidase-tqjs had similar efficacy to intravenous administration.
An overview of the potential treatment strategies for patients were presented at the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Promising abstracts surrounding DLL3 targeting for patients with lung and neuroendocrine cancer were presented at WCLC 2024.
As of May 2024, follow-up and exploratory analyses of MARIPOSA show improvements in outcomes for patients with EGRF-mutated non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).

In a session at the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer, presenters highlight the most significant developments in local therapy for metastatic non–small cell lung cancer and advanced disease.
An overview of the latest developments in targeting DLL3 in lung neuroendocrine tumors were presented at the 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Highlights from multiple trials investigating novel treatments for mNSCLC were presented at 2024 World Conference on Lung Cancer.
Presentations highlighted the potential of tarlatamab in treating solid tumor cancers.
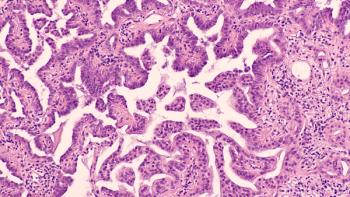
Datopotamab deruxtecan was effective in patients with TROP2-QCS biomarker-positive tumors for non–small cell lung cancer