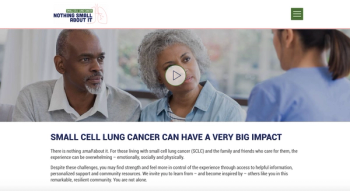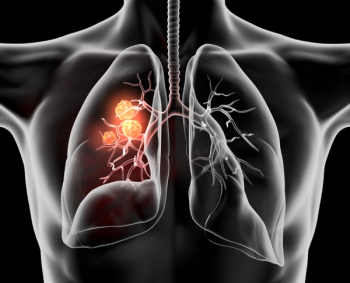
The investigators found that the combination of cemiplimab-rwlc and chemotherapy resulted in a substantial improvement in OS compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with metastatic or locally advanced disease and tumors with either squamous or non-squamous histology and across all programmed death-ligand 1 expression levels.