
According to the study, 20% of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms progress to blast phase.

According to the study, 20% of patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms progress to blast phase.
Researchers applied extracellular vesicles retrieved from human red blood cells to serve as natural carrier to deliver the anti-cancer antisense oligonucleotides to the tumor site.
LBL-034 could be best in class in treating individuals with multiple myeloma.
If approved, zongertinib may be a new first-line oral tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) for patients with HER2-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), a transformative step in TKI drug development.
If accepted, daratumumab would be the first approved treatment for smoldering multiple myeloma.
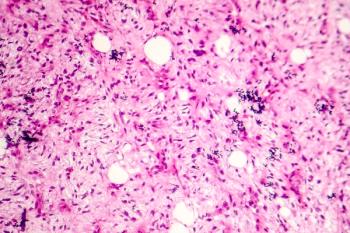
Brigimadlin is a new oral MDM2-p53 antagonist under investigation as a potential first-line therapy to improve outcomes for patients with advanced or metastatic dedifferentiated liposarcoma.

Anthony Perissinotti, PharmD, BCOP, discusses unmet needs and trends in managing chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), with an emphasis on the pivotal role pharmacists play in supporting medication adherence and treatment decisions.

The analysis also found that the intervention methods could improve patients’ physical, cognitive, and emotional functioning.

Pharmacy teams are learning to adapt to the challenges of limited distribution networks and orphan drug designation in oncology, with integrated pharmacy support playing a crucial role in enhancing patient access and adherence.
Expanding operations to provide specialty infusions can provide benefits to both patients and oncology practices.
Increased bone marrow adiposity is associated with progression of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) to multiple myeloma.
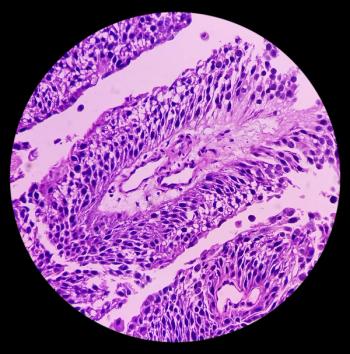
Patients with low-grade intermediate-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer who achieved a complete response rate after 3 months of UGN-102 treatment had an 82.3% duration of response at 12 months.

The findings show robust connections between symptoms, with variations in depression scores directly or indirectly influence fatigue and other symptoms.

Less than 16% of high-risk lung cancer individuals have heard or discussed lung cancer screenings with a health care provider.
Using in vitro models, study investigators predict the risk of bone metastasis in breast cancer based on correlations with their in vivo behaviors and potential.

Pegfilgrastim (Neulasta; Amgen) treats neutropenia that is caused by cancer medications and helps the bone marrow to create new white blood cells.

Pharmacists play a critical role in treating patients with breast cancer and can help address their social determinant of health challenges.
Two clinical trials with MRD monitoring may be practice changing: TRACERx and AEGEAN.

ASCO is prioritizing the expansion of pharmacist involvement in its organization by recognizing pharmacists' contributions to safety standards, quality improvement initiatives, and certification programs.

If approved, the combination regimen would be the first FDA-approved treatment for adults with recurrent KRAS mutant low-grade serous ovarian cancer (LGSOC).
Gut microbiome research is no longer an obscure field in cancer care.

Following lung cancer diagnosis, adjusting lifestyle habits can improve treatment responses.
Further efforts may be required to urge eligible members of the public to get screened for lung cancer.

A patient with BPDCN finds her champion.

Targeted therapies, CDK4/6 inhibitors, and precision medicine are improving outcomes for patients with high-risk and metastatic disease.

Rising cancer rates and costs pose challenges in global oncology markets amid AI and targeted therapy breakthroughs.

Experts from Moffitt Cancer Center discuss the benefit of multidisciplinary teams in lung cancer care.

The 2024 NCODA International Fall Summit took place in Orlando, Florida, from October 23 to October 25.

HLX14 (Organon) is an investigational biosimilar to denosumab (Prolia/Xgeva; Amgen).
Advancements include novel combination therapies and improved diagnostic techniques.