
Non–FDA-approved medications may be accessed for patient care via 3 alternative pathways: expanded access, the Right to Try Act, and off-label use, which are reviewed in this article.

Non–FDA-approved medications may be accessed for patient care via 3 alternative pathways: expanded access, the Right to Try Act, and off-label use, which are reviewed in this article.
The story of pinksocks and the inspiring movement that they launched.

In a study, RK-33 demonstrated positive effects against the protein DDX3, which is key in the growth of cancer cells and spreading of disease.
Zolbetuximab is the first approved CLDN18.2-targeted treatment for gastric and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma.
The tool can detect cell changes and mutations that drive resistance and relapse.
Awareness of uterine fibroids and uterine fibroid embolization can prevent unnecessary hysterectomies, especially in Black women, who are more likely to have uterine fibroids.
This review discusses the significance of the FDA-approved drug inotuzumab ozogamicin in pediatric patients with acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) and relapsed/refractory (R/R) ALL, and the evolving therapeutic options in R/R ALL.
Compared with brentuximab vedotin and chemotherapy, nivolumab and chemotherapy had longer progression-free survival and a better safety profile.
This retrospective cohort study provides preliminary evidence for safe removal of mesna from VAdriaC cycles, as the incidence of hemorrhagic cystitis did not increase in patients with Ewing sarcoma who received cyclophosphamide without prophylactic mesna.
HER2-mutant NSCLC is associated with poor prognosis. Zongertinib and BAY 2927088 are HER2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors that have activity in NSCLC with manageable toxicity profiles.
The KEYNOTE-756 and CheckMate 7FL trials show this combination improves pathological complete response rates in this patient population.
The results indicate the potential use of loncastuximab tesirine as a treatment option for the rare hyperinflammatory condition.

Artificial intelligence holds immense potential to address the rising demand for oncology services and improve patient outcomes by facilitating more effective, efficient, personalized cancer care.
The drug's safety profile included significant rates of nausea, vomiting, and hematologic toxicities like neutropenia and thrombocytopenia. Although promising, brigimadlin requires careful management of adverse effects, including antiemetic and hematologic support.

Although respondents identified some exciting areas of growth, challenges remain, including the complex insurance system and ensuring patient medication adherence.

Shirish Gadgeel, MD, discusses an integrated analysis of the regional TRUST-I study and global TRUST-II study presented at the European Society for Medical Oncology Congress 2024.

Behind The Script is a photo submission campaign designed to feature real pharmacists with candid, HIPAA-compliant photos to celebrate American Pharmacist Month.

The authors of these peer -reviewed papers collectively emphasize the evolving landscape of oncology treatment.

This Women Pharmacists Day, Jolynn Sessions, PharmD, BCOP, FHOPA, discussed the crucial role of women in pharmacy.

Terry Keys highlights the role of language and terminology as barriers for patients receiving cancer care.
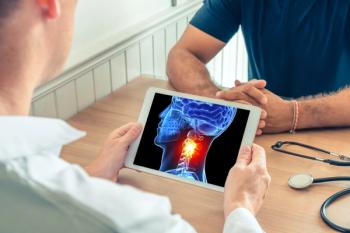
The trial met its primary endpoint of event-free survival, furthering treatment options for resected, locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.

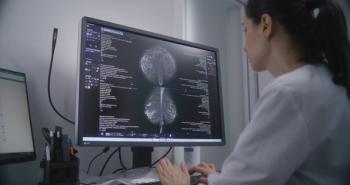
A breast-level artificial intelligence score may be able to estimate the risk of future breast cancer, allowing for patients to take preventative measures.

Pharmacists also help patients manage their adverse effects and treat patients to live healthy lives.

Nadine Barrett, PhD, MA, MPH, discusses the role of international collaborations to advance global cancer care access.

Naoto T. Ueno, MD, PhD, FACP, discussed the role of the Hawaiʻi Cancer Consortium to advance trial and treatment efforts for patients with cancer.

The FDA also approved the FoundationOne Liquid CDx assay as a companion diagnostic device to identify patients who would benefit from the treatment.

Shirish Gadgeel, MD, discusses the promising results of the randomized phase 3 HARMONi-2/AK112-303 study comparing ivonescimab to pembrolizumab in PD-L1–positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
The real-world study results of ciltacabtagene autoleucel are comparable to data from the CARTITUDE-1 trial, emphasizing its efficacy and safety.

Longer-term data from the phase 3 MARIPOSA trial confirm superior outcomes of a chemotherapy-free amivantamab-vmjw plus lazertinib regimen compared to osimertinib monotherapy as first-line therapy.