Top five most popular articles this week on Specialty Pharmacy Times.

Top five most popular articles this week on Specialty Pharmacy Times.

Researchers from the VA system examined how mail-order delivery of drugs affects their patients with HIV.
Marker helps differentiate dormant HIV-infected cells from their health counterpart cells.

The US Veterans Administration (VA) health care system is the largest in the United States, serving 22 million former military members.

Antibody therapy enables efficacious control of HIV-like virus in monkeys.
Round 2 of study finds a reduction in start time of antiretroviral therapy for HIV treatment.

Although dolutegravir (DTG) is known for its high genetic barrier to resistance, its durability to maintain virologic suppression had not previously been evaluated.
Insulin could become a new therapeutic option for HIV-associated neurocognitive disorders.

Clinicians should screen all newly diagnosed HIV patients for tuberculosis.

Hypertension can cause cardiovascular risk factors in patients with HIV.
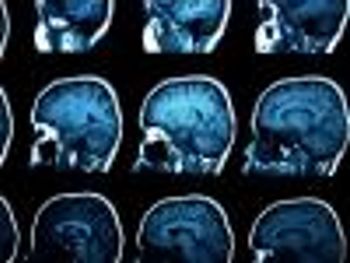
Brain scans could help diagnose patients with HIV-related cognitive issues.

An integrin is a receptor protein attached to cells that aid in allowing the cell to react to the extracellular matrix.

Tuberculosis (TB) and HIV are 2 of the deadliest diseases worldwide, with TB recently reaching the top of the list in 2014.

Genital herpes is associated with increased risk of HIV transmission.

Top articles of the week on Specialty Pharmacy Times.
Non-inferiority found between tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and tenofovir alafenamide regimens.
Regimens with Descovy show non-inferiority to those containing Truvada.

Top news of the day from across the health care landscape.
Scientists continue to pursue the development of an HIV cure.
Synovial CD4+ T cells that produce IL-21 play a role in joint inflammation.

Among the general population, roughly 5% of people develop seborrheic dermatitis. However, seborrheic dermatitis affects 85-95% of patients with HIV.
A subset of the HIV is transmitted to the child during pregnancy or through breastfeeding.
HIV transmitted to a child is less likely to be killed by CD4 helper T cells.

A novel nanotechnology approach can reduce HIV treatment dosages and improve drug delivery, according to a study.

A New Zealand woman who was intentionally infected with HIV and was the center of a high profile criminal case faces down numerous challenges related to the virus.