Researchers from Saint Louis University Medical Center will test the safety and efficacy of sofosbuvir and ribavirin in children with hepatitis C.

Researchers from Saint Louis University Medical Center will test the safety and efficacy of sofosbuvir and ribavirin in children with hepatitis C.
Four children who recently died have tested positive for enterovirus D68, though it is not yet clear what role, if any, the virus played in their deaths.

ADHD medications are prone to the same abuse, misuse, and diversion as opioids.

Enterovirus-D68 could soon be in the rearview mirror, according to a Hartford, CT, pediatric intensivist who has treated more than 20 children hospitalized with the infection.
In many cases, children between the ages of 6 months and 8 years should receive 2 doses of the influenza vaccine separated by a minimum of 4 weeks.
Influenza boosts the ability of pneumococci to cause middle ear and throat infections.

Respiratory illness now confirmed in 27 states, with significant growth expected in coming weeks.
Clinical pharmacists can reduce anti-epileptic drug (AED) prescription errors that commonly result from incomplete or poor documentation.

Combined with bolus insulin aspart (NovoLog), insulin degludec (Tresiba) improves long-term glycemic control in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes.
The severe respiratory virus that is hospitalizing children across the United States has now been confirmed in 17 states.

Just a dozen drug ingredients are the culprits behind nearly half of all emergency hospitalizations for unsupervised prescription drug ingestions among young children.
The FDA has granted approval for the use of hemophilia B treatment Rixubis in pediatric patients.

The respiratory virus that hospitalized hundreds of children in the Midwest and the South has now reached the Northeast.
Roughly 1 in every 3 obstetric complications are related to preeclampsia.

A single dose of intramuscular peramivir (Rapivab) alleviated the symptoms of influenza in 2 clinical trials.
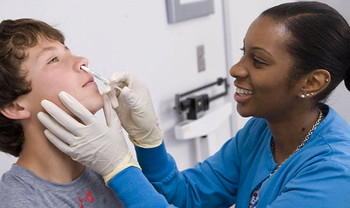
The short shelf life of the live attenuated influenza vaccine may contribute to patients unwittingly receiving an expired dose.

The FDA has approved the use of Sanofi's Menactra vaccine as a booster immunization against meningococcal disease in patients at continued risk.

Outbreak of enterovirus D68 spreads to several states across the Midwest.
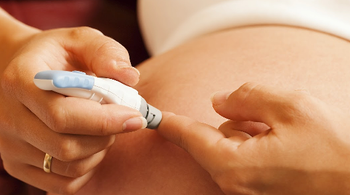
Adolescents exposed to gestational diabetes in utero have a higher risk of developing impaired glucose tolerance.
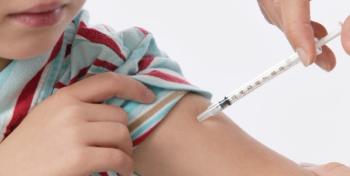
Vast majority of parents are opting for their young children to receive potentially lifesaving vaccines despite the controversy surrounding their right to refuse such immunizations.
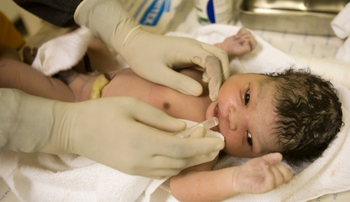
Ceasing treatment may be the only way to determine whether HIV is cured, but doing so carries long-term risks.

Roughly one-third of teen girls' clinicians and almost half of teen boys' clinicians did not recommend HPV vaccination in 2013.


Children who grow up in stressful settings are at higher risk of developmental problems that may later manifest as chronic disease. Fortunately, support programs may help reduce stress and improve outcomes.

With its expanded approval of Lumizyme (alglucosidase alfa) to treat all Pompe disease patients, regardless of age or time of disease onset, the FDA has eliminated the Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy program that restricted the drug's use to those aged 8 years or older with late-onset disease.