C. difficile
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News
Study Data Suggest That Cancer, Irritable Bowel Disease Are Associated With Risk of C Diff Infection
Patients who are immunocompromised generally had worse risk and severity of CDI.
With a new administration protocol created specifically for the routine clinic, infectious disease physicians can treat recurrent clostridioides difficile infection in less than 3 weeks.
Among individuals who received systemic antibiotics within 8 weeks, 6 months, 12 months, and 24 months of receiving fecal microbiota, RBX2660 prevented recurrence.
Health-related quality of life scores were positively associated with log MHI and Bacteriodia, and negatively with Gammaproteobacteria and Bacilli.

Treatment-emergent adverse events associated with Rebyota for Clostridioides difficile infection were more prevalent in those with renal comorbidities than in those without and were moderate in severity as well as related to pre-existing conditions.
Study is the first to compare SARS-CoV-2–associated sepsis and presumed bacterial sepsis on mortality and incidence.
Not only did enterococci promote C. difficile pathogenesis, but it was also shown to provide fermentable amino acids, facilitating its virulence agitated gastrointestinal tracts.
Although antibiotics are the standard-of-care treatment for Clostridioides difficile infection, they can cause further microbiota changes that predispose patients to recurrence.

Investigators said that understanding virulence factors, resistance mechanisms, and host interactions can help establish the development of novel therapeutics for Clostridioides difficile.
Using metagenomic information, the technology isolates phages whose enzymes can specifically target the bacteria that causes C. difficile infection.
Investigators will continue to research RBX2660 in patients who are immunocompromised or who have chronic conditions with Clostridioides difficile infection.
Prior studies had produced conflicting results on whether the pandemic positively or negatively impacted health care-associated C. difficile infections, yet the results of this current study indicate the pandemic played a limited role.
New innovations are revolutionizing diagnostics and optimizing treatment outcomes, marking significant strides in the fight against digestive diseases.
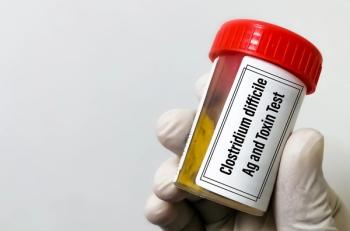
CDI is difficult to contain in health care settings because some patients are unknowing carriers of the toxigenic strains of the infection.

Antibiotic prescribing at hospital discharge is a component of pharmacist-led antimicrobial stewardship programs that is often overlooked.

Clostridioides difficile infection was found to increase the risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality in a recent study.

The data could inform how non–steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-mediated mitochondrial uncoupling could affect other diseases.
For many patients with C diff, the experience of medical gaslighting is a common one because many health care providers lack education and familiarity with the disease.
Pharmacist-led discharge stewardship initiatives have shown promising results.

Data show these cases pose some of the most significant threats to patients and health systems.

MicroRNA has shown the potential to more effectively and accurately identify C. difficile infections and manage it after diagnosis.

Fecal microbiota transplantation is a process that restores bacterial diversity in the gut microbiome after standard-of-care antimicrobial therapy.

Clostridioides difficile infection can be difficult to treat, but increasing disease awareness can improve screening and treatment outcomes.

As one of the most trusted health care professionals, pharmacists play a vital role in debunking medication myths by providing patients with accurate information to make positive decisions regarding their health.