Growth Differentiation Factor-15: A Multifaceted Player in Prostate Cancer Biology and Therapeutic Targeting
Key Takeaways
- GDF15 is markedly upregulated in advanced prostate cancer and integrates stress, inflammatory, and malignant signaling with metabolism, immunity, and survival programs that reinforce tumor persistence.
- Metabolic reprogramming driven by GDF15 includes mitochondrial regulation and oxidative stress responses, enabling adaptation to hypoxia and nutrient deprivation and promoting metabolic plasticity.
GDF15 can reshape prostate cancer prognosis and treatment; pharmacists track emerging biomarker panels and targeted therapies for metastatic disease.
Prostate cancer remains one of the most commonly diagnosed malignancies among men worldwide and continues to represent a significant cause of cancer-related morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in early detection and treatment, advanced and metastatic disease remains difficult to manage, particularly due to therapy resistance and disease heterogeneity. The lack of precision in making prognoses based upon traditionally used biomarkers, such as prostate-specific antigen (PSA), has led researchers to seek new molecular markers. Recent research on the multi-faceted potential of growth differentiation factor 15 (GDF15) has identified it as an important target in prostate cancer.1,2
Biological Role of GDF15 in Prostate Cancer
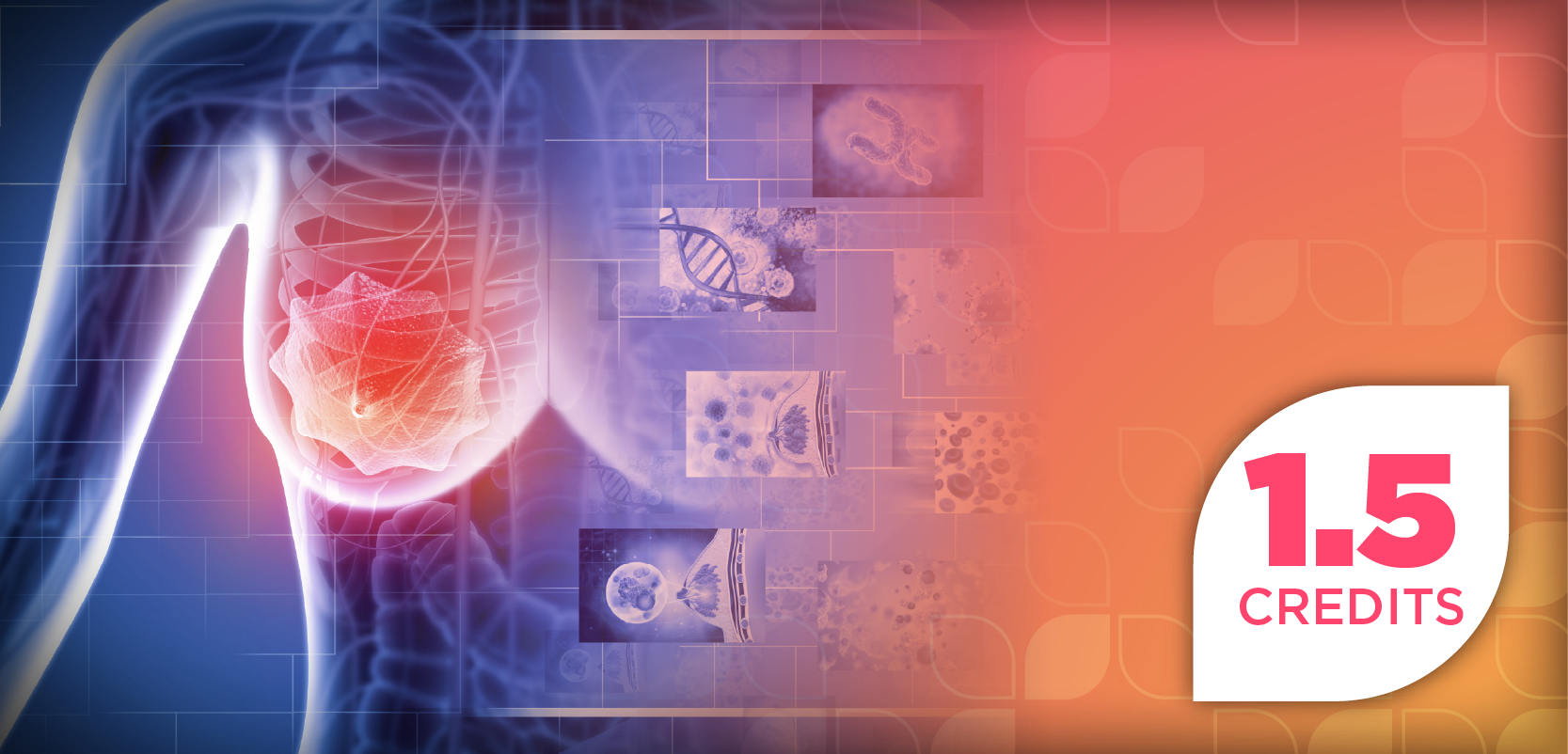
GDF15—a member of the transforming growth factor–β superfamily—is often induced under stress, inflammation, and malignancy pathways.2 GDF15 expression is highly upregulated in prostate cancer tissues and the blood, especially during the advanced stages. GDF15 has been shown to play a role in the regulation of metabolism, immunity, and survival pathways that all combine for the development of the tumor.1,2
A recent review published in the Chinese Medical Journal comprehensively describes how GDF15 influences tumor metabolism and adaptation to stress, enabling cancer cells to thrive under hypoxic and nutrient-deprived conditions.2 By regulating mitochondrial function and oxidative stress responses, GDF15 supports metabolic plasticity that favors tumor growth and persistence.
Contribution to Tumor Progression and Metastasis
Its ability to facilitate metastasis, particularly to the bone, has long been a hallmark of lethal prostate disease. Currently, GDF15's functions in the promotion of metastatic spread are increasingly being recognized.2 Preclinical research demonstrates GDF15’s role in enhancing motility, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells, thereby enabling their migration into other tissues.2
Additionally, GDF15 also regulates the tumor microenvironment via modification of stromal and immune cell composition. Overexpression of GDF15 in cancer is known to generate a conducive microenvironment facilitating tumor engraftment and survival via cytokine receptors and extracellular remodification.1
Clinical Significance and Biomarker Potential
Knowledge of the clinical application of GDF15 as a biomarker is gaining increasing attention. For example, increased circulating levels of GDF15 have been shown to be related to metastatic disease, poor prognosis, or decreased overall survival. Such approaches offer potential improvement over serial measurements of PSA alone.1,2
Several studies also suggest that GDF15-based panels can aid in the distinction between indolent and aggressive diseases, therefore avoiding overtreatment of low-risk patients and facilitating the identification of those who are likely to require early treatment.1
This form of GDF15 targeting represents a new therapeutic strategy for prostate cancer. Experimental monoclonal antibodies and pathway inhibitors directed against GDF15 signaling are also under investigation. These agents aim to reverse cachexia, restore chemosensitivity, and enhance immune responsiveness.2
New approaches combining GDF15 inhibitors with chemotherapy, androgen deprivation therapy, or immunotherapy could achieve synergistic results. Further research is necessary to understand the timing of treatment, patient selection, and long-term safety.
Conclusion
GDF15 has been identified to play a pivotal role in prostate cancer, including aspects like progression, metastasis, chemotherapy resistance, and immune response. Recent clinical and preclinical studies have provided evidence for its promising roles as a prognostic and therapeutic tool. As additional evidence is uncovered in its molecular basis, GDF15 is likely to feature prominently in precision medicine approaches targeting advanced prostate cancer.
REFERENCES
Chinese Medical Journal article review decodes GDF15 in prostate cancer metabolic character and therapies. EurekAlert! Published January 30, 2026. Accessed February 5, 2026.
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/1114726 Zhu W, Xu H, Xiong X, et al. Decoding GDF15: Impact on prostate cancer metabolism, chemoresistance, and clinical applications. Chinese Medical Journal. 2025;139(2):211-221. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000003876
Newsletter
Stay informed on drug updates, treatment guidelines, and pharmacy practice trends—subscribe to Pharmacy Times for weekly clinical insights.