
For those with unexplained pregnancy loss, these results could prove promising improvements to birth outcomes.
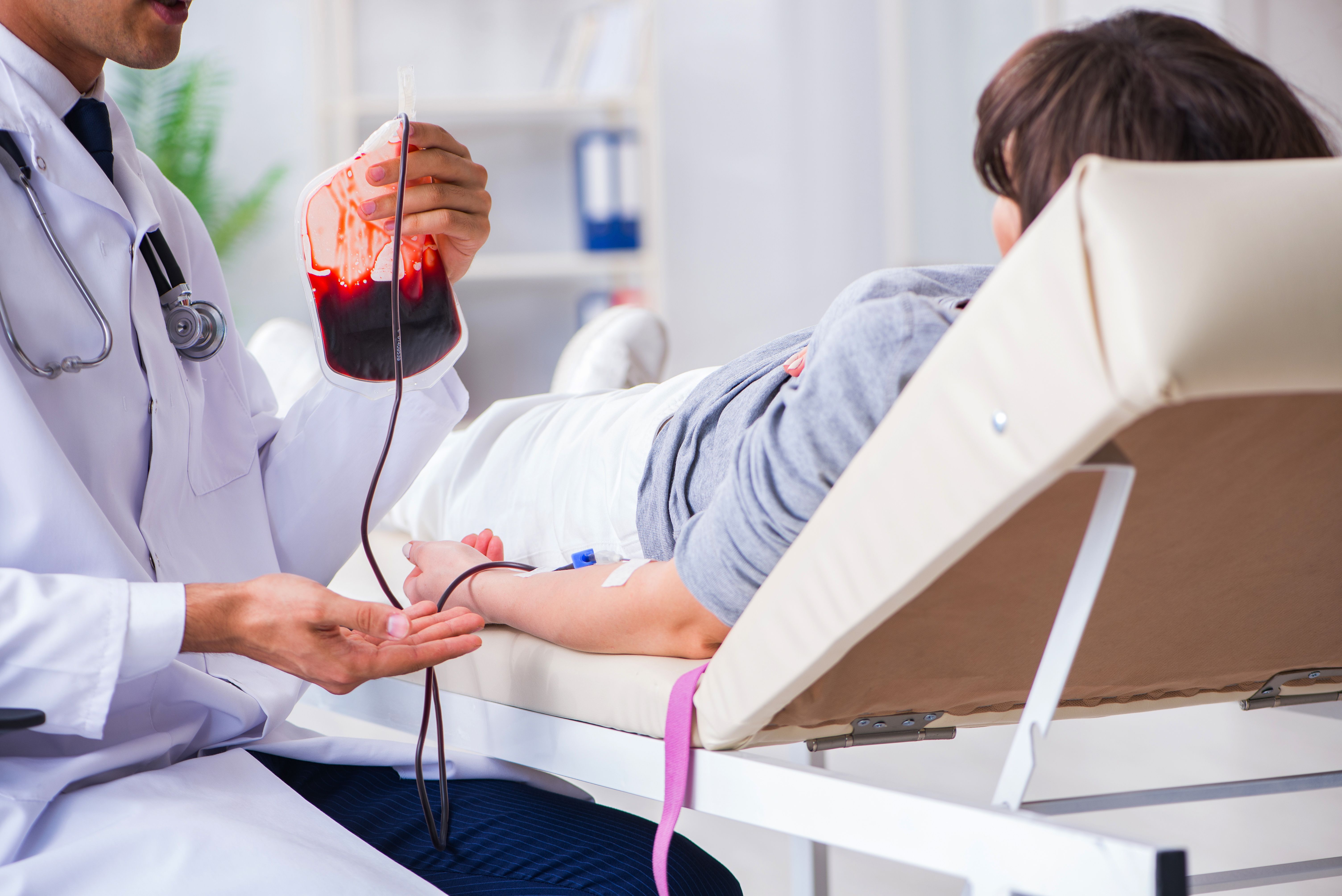

For those with unexplained pregnancy loss, these results could prove promising improvements to birth outcomes.
The use of intravenous immunoglobulin led to positive protective effects on osteoporosis.
Noticing indicators of IVIG non-responsiveness can lead to better outcomes among patients with Kawasaki disease as treatment is adjusted.
Investigators analyzed a series of disease-modifying therapies in a multi-decade trial.
Response to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment and analysis of neurofilament light chains in patients could be used as prognostic indicators of Guillain-Barre syndrome.
The systematic review summarized all available evidence on the subject, finding that intravenous immunoglobulin could have a role in treatment.
Intravenous Immunoglobulin as a therapy for patients with pyoderma gangrenosum could open new treatment avenues for the rare and challenging condition.

Two different brands of intravenous immunoglobulin have been investigated, finding Brand P led to significantly longer durations of fever and hospitalization when compared to brand T.
In an analysis of 16 immunocompromised patients with COVID-19, intravenous immunoglobulin was effective and associated with clinical cure.
The presence of glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies in intravenous immunoglobulin can lead to a misdiagnosis of type 1 diabetes mellitus if a false-positive result is garnered.
By functioning as an antibody replacement therapy, IVIG can be used to manage a wide range of inflammatory and autoimmune disorders.
A lack of widespread hepatitis B screenings compound with the issue of inaccurate test results, which can complicate treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin.
It is essential for clinicians to properly diagnose patients with suspected AVWS and provide them proper treatment, which could be intravenous immunoglobulin.
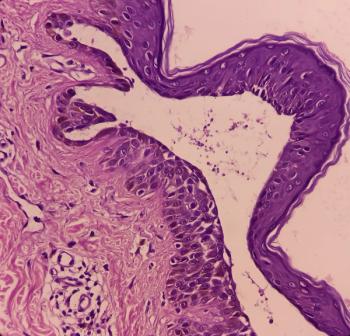
A patient with severe and recurrent pemphigus vulgaris achieved lasting remission with a novel intravenous immunoglobulin preparation that had the added benefit of reducing treatment-related side effects.
Intravenous immunoglobulin was effective as an adjunctive treatment to anticoagulation in a patient with post-viral platelet-activating anti-PF4 disorder, indicating the need for accurate diagnosis and treatment selection.
By developing the Shizuoka score, which features a new predictive model using machine learning, patients with Kawasaki disease who are non-responders to intravenous immunoglobulin were able to be accurately identified.
In a rare case of non-tumor anti-Tr/DNER antibody-associated ataxia, the patient is treated with plasmapheresis and intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) for symptoms such as dysarthria and difficulty walking.

With this approval, Yimmugo is the first approved product from the Biotest Next Level production facility.
The IVIG therapies were previously approved for 4-week room temperature storage conditions of 25º Celsius during the first 24 months of shelf life.
Bivigam was initially approved by the FDA in May 2019 for the treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency, including a group of genetic disorders.

The approval marks the first and only once-daily target therapy for generalized myasthenia gravis for self-administration in this patient population.

Choice of therapy should be selected based on patient needs and conditions.
Intravenous immunoglobulin could potentially be given throughout the duration of anti-BCMA bispecific antibody therapy for the treatment of multiple myeloma.

Intravenous immunoglobulin found to provide fast and long-lasting relief for COVID-19-related neurological conditions, although investigators are still uncovering the pathology of many of these conditions.

The analysis results showed no statistically significant impact on either outcome, but results from prior prospective studies suggest that intravenous immunoglobulin may lengthen hospital stay for patients with severe COVID-19.