COVID-19
Latest News

Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

The results of a new UCLA-led study show that the pandemic has exacerbated disparities in care, widening inequities.
But study results show some are not sold on performing the task; adequate training can build their confidence.
The study will have 3 cohorts examining different regimens of the current Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine or an omicron-based vaccine and will use participants from the phase 3 COVID-19 booster study.

The findings suggest that pregnant women should not delay COVID-19 vaccination until late pregnancy.

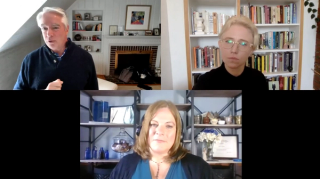
Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates at the American Pharmacists Association (APhA) and executive director of the APhA Foundation, discusses the results of a nationwide survey of pharmacists during the ongoing pandemic.
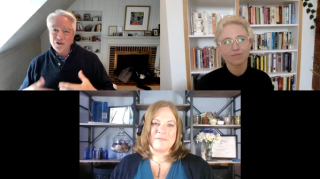
Key opinion leaders provide some advice for the public regarding COVID-19 booster shots and look to the future of the pandemic.
Drs Angela Rasmussen and Donald Alcendor detail the roadblocks facing COVID-19 booster shots.
Gaps in vaccination rates may be related to access and not just distrust and skepticism, investigators from Ohio State University find.

New study results show that of those who tested or were presumed positive for SARS-CoV-2, 44% developed neurological symptoms.
Investigators learned that the degree of response depended on whether an individual has had 1, 2, 3, or 4, exposures through infection, vaccination, or both.
Some study limitations include that follow-up data were missing for some patients who dropped out of the study during the follow-up stages and the timing of the follow-up echocardiograms were random and driven by preference versus standard protocol.

The kit helps detect SARS-CoV-2 RNA in nasopharyngeal, anterior nasal, mid-turbinate nasal or oropharyngeal swab specimens from individuals suspected of COVID-19 by their health care provider.
Both data sets confirm previously announced results showing that the boost protects against the variant.
Investigators say that the post-acute sequalae markers are Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA levels in the blood, pre-existing types 2 diabetes, the presence of certain antibodies, and SARS-CoV-2 RNA levels in the blood.
Investigators analyzed data to determine the outcomes and risk factors for severe cases and how individuals with inflammatory bowel disease are affected.
New study results show that there are more incidences of this inflammation of the heart muscle related to not being vaccinated than there are to the vaccine itself.
Having such a program spearheaded by pharmacists has helped show the public the vital roles that pharmacists play.

The FDA also expanded the pediatric emergency use authorization for remdesivir to include the treatment of non-hospitalized pediatric patients at high risk of disease progression.
This recent research also found that those who received the Moderna vaccine were less likely to be hospitalized compared to recipients of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine.

Stanford Medicine investigators were able to estimate who is most likely to land in the hospital.

Results of an analysis show that 3 doses of either Oxford/AstraZeneca COVID-19 or Pfizer BioNTech COVID-19 neutralizes the variant.
Further, the Index is based on proprietary data from PCR testing services administered by Walgreens.

Shreejit Nair, senior vice president and life sciences market business lead at CitiusTech, discussed what the impact of the pandemic has been on the advancement of data interoperability in health care.

A sizable number of clinical trial participants say they had at least 1 AE, with fatigue and headaches the most common.
The analysis describes cost-effective options for individuals without symptoms and recommends isolation strategies to help policymakers safeguard against resurgences.