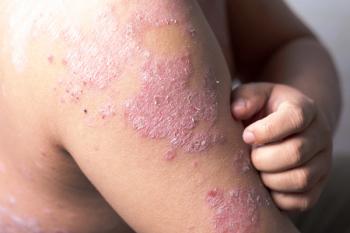
In addition to current treatment regimens, 2 experts discuss how available options can vary between adult and pediatric patients.
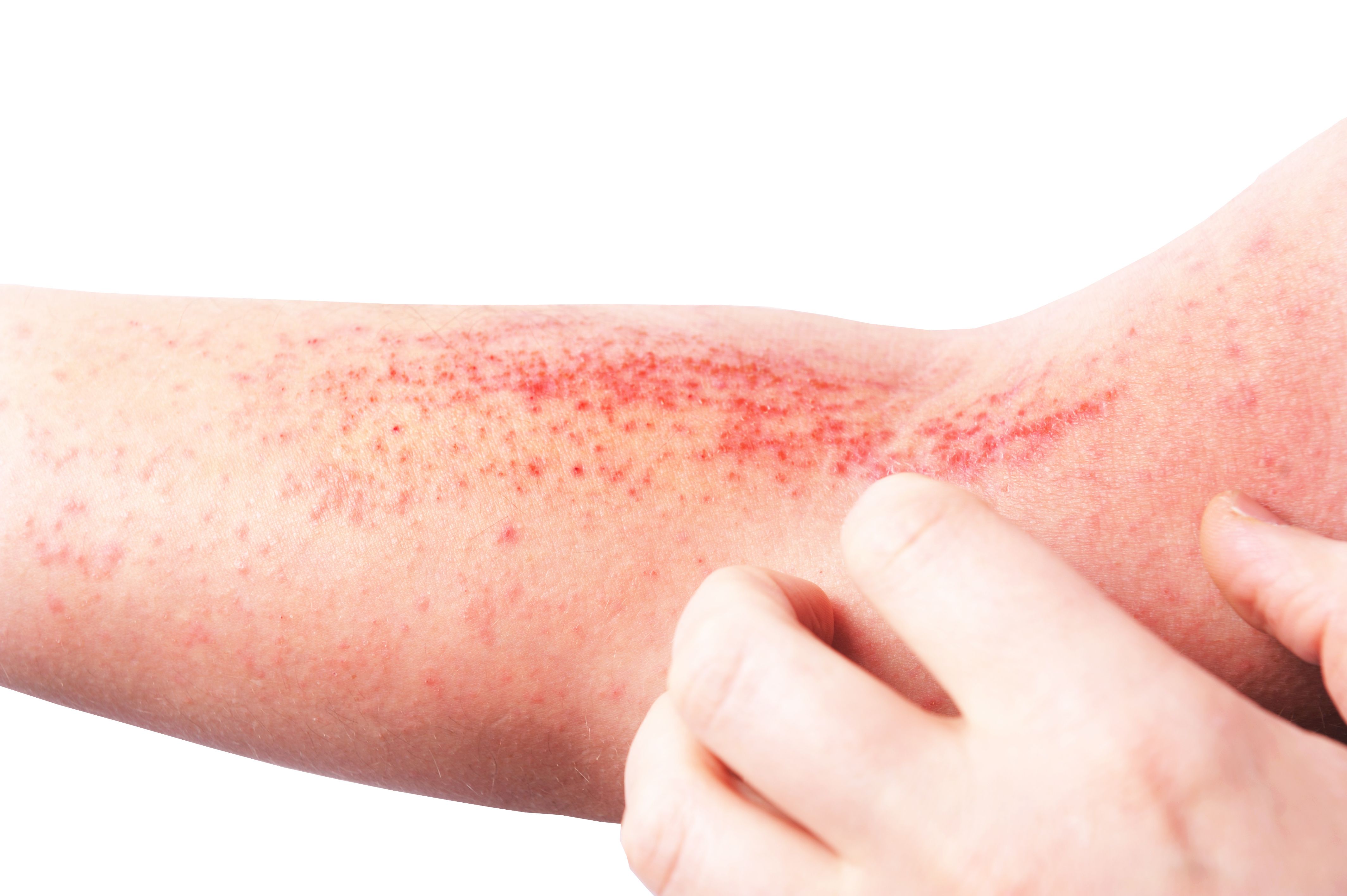

In addition to current treatment regimens, 2 experts discuss how available options can vary between adult and pediatric patients.
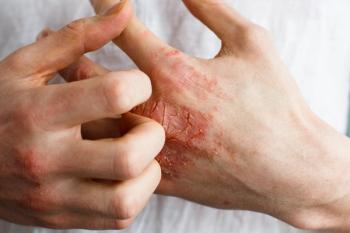
In addition to highlighting the difficulties patients face when managing plaque psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, 2 experts describe how pharmacists play a crucial role in treatment.

Treating older patients requires a greater focus on treating their AD without exacerbating their comorbidities.
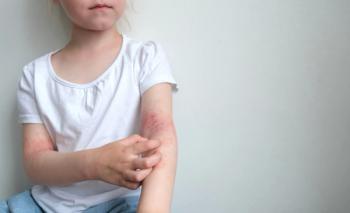
It's key for clinicians to optimize therapy prior to systemic agents.

A supplemental New Drug Application will be submitted for roflumilast cream 0.05% for the treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in children 2 to 5 years of age.
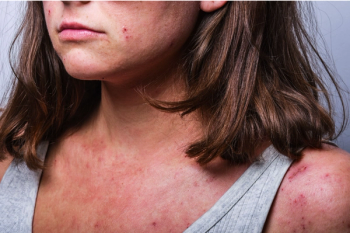
Acne, atopic dermatitis, rosacea, urticaria, and sunburn present differently and require specific management.
The treatment improved lung function at 12 weeks and quality of life at 4 weeks.

Clearer skin on the face and hands lasted 1 year into treatment.

Pharmacists play key roles in navigating prior authorizations and other limits on utilization, as well as educating and listening to patients and caregivers.

The primary outcome of the study includes an IGA score of 0 or 1, which indicated clear or almost clear skin, respectively, with a reduction, from baseline to week 16.

Expanded indication for abrocitinib (Cibinqo; Pfizer Inc) includes patients 12 to <18 years of age with refractory, moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis that is not adequately controlled with other systemic medications.
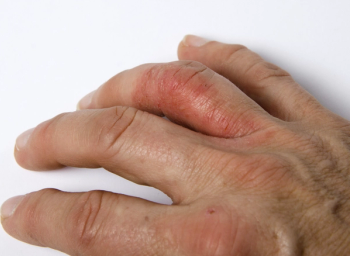
Greater prevalence of hand eczema among health care professionals working in COVID-19 units linked to increased hand sanitation habits.
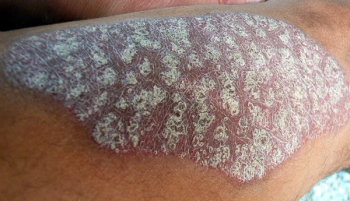
Clinical trials show that patients with atopic dermatitis experienced improved symptoms with dupilumab starting at 8 weeks, with maximum effect around 12 weeks.

All primary and ranked secondary endpoints of the study were met at week 16, which were sustained or improved through week 24 and were coupled with patient-reported improvements compared with placebo in treating psoriatic arthritis.
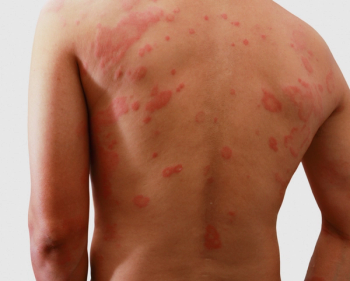
The goals of therapy for atopic dermatitis include reducing symptoms of pruritis and dermatitis with disease control and prevention of flares.

ADvocate 1 and ADvocate 2 are 52-week randomized, double-blind phase 3 studies designed to evaluate lebrikizumab as monotherapy in adult and adolescent patients with moderate to severe AD.
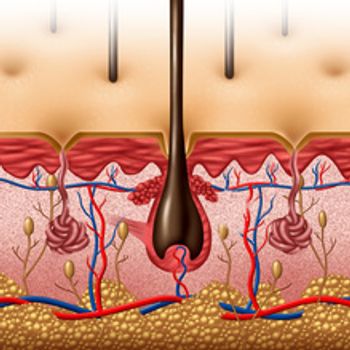
Researchers discovered that a common anti-inflammatory drug could lower the number of patients on ventilators from COVID-19, increasing the likelihood of survival by more than 50%.
Guidelines provide information on the management and treatment of this common skin condition.
Lebrikizumab is a novel monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity to the IL-13 protein to prevent the interaction between IL-13Rα1 and IL-4Rα, which blocks downstream signal activation along the IL-13 pathway.

Approval in this patient population makes dupilumab the first and only biologic medicine approved for the treatment of moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis from infancy through adulthood.
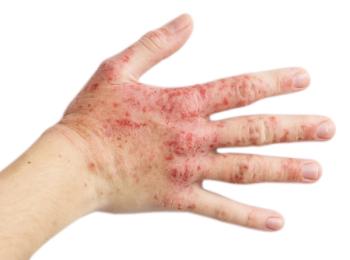
The FDA has approved abrocitinib tablets to treat adults with moderate-to-severe, refractory atopic dermatitis.

Among individuals taking the medication with standard-of-care topical corticosteroids, approximately 41% achieved clear or almost clear skin at 16 weeks.
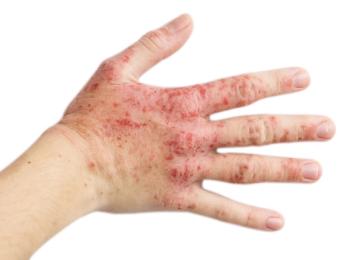
The monotherapy demonstrates rapidly improved symptoms over 4 weeks for individuals with moderate-to-severe disease.
Study finds that the use of biologics and other potentially immunocompromising therapies for atopic dermatitis was associated with low risk of severe COVID-19.

This month's featured products include treatments for insomnia, atopic dermatitis, and more.