Cholangiocarcinoma
Latest News
Latest Videos

CME Content
More News

Biliary tract cancers have become the model for precision oncology because of its complex molecular landscape.
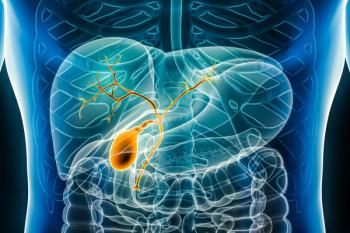
Specific data and results for pembrolizumab in patients with advanced or unresectable biliary tract cancer will be presented at an upcoming medical meeting and will be submitted to regulatory authorities.
Distinguishing between atypical hepatocellular carcinomas and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma can be difficult, but researchers identified several reliable MRI features to assist in differentiation.
From newsworthy moments to groundbreaking research, these are the most popular articles in the cholangiocarcinoma space, published on Pharmacy Times® during 2022.

Recommendations for the management of bile duct cancer benefit authorities, patients, and physicians, but investigators say more research is needed.
The median progression-free survival and overall survival were 7.4 and 14.7 months, respectively, in chemotherapy-naïve patients with advanced or recurrent biliary tract cancer.
Study findings may make durvalumab plus chemotherapy a new standard of care option for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer.
Percutaneous Hepatic Perfusion Procedure May Extend Life for Patients With Inoperable Cholangiocarinomas
PHP shows promise extending survival in patients with inoperable intrahepatic cholangiocarinomas or extrahepatic cholangiocarinoma with liver metastases.
The investigational drug is a monoclonal antibody with a high affinity and specificity for cancer-specific plectin, a cell surface protein that correlates with aggressive tumors and poor prognosis.

Derazantinib Shows Clinical Benefit, Manageable Safety Profile in Patients With Cholangiocarcinoma
Derazantinib is an investigational oral inhibitor of FGFR1, FGFR2, and FGFR3 in patients with locally advanced or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Investigators also confirmed that FGFR2 fusion–positive tumors have a higher expression of FGFR2 but were not associated with higher expression of FGFR1, FGFR3, or FGFR4.
Promising data suggest triplet regimens may more effectively treat patients with unresected and metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.

A compound often found in citrus fruits, nobiletin, could be a less toxic and more effective treatment for cholangiocarcinoma.
Inflammation-based prognostic scores can be a valuable tool in assessing the overall survival of patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.

FDA Grants Accelerated Approval to Futibatinib for Locally Advanced, Metastatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Futibatinib (Lytgobi, Taiho Oncology, Inc) is indicated for adult patients with previously treated, unresectable, locally advanced or metastatic intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma harboring FGFR2 gene fusions or other rearrangements.

FDA to evaluate New Drug Application for futibatinib in the treatment of patients with previously treated locally advanced or metastatic cholangiocarcinoma.
The approval of Tibsovo marks the first and only targeted therapy approved for patients with previously treated IDH1-mutated cholangiocarcinoma.
Cholangiocarcinoma is a rare bile duct cancer, with physicians diagnosing approximately 8000 cases each year.
A supplemental new drug application has been submitted to the FDA for ivosidenib tablets (Tibsovo) as a potential therapeutic option for patients with previously treated, IDH1-mutated cholangiocarcinoma.

Data from a phase 1b/2 trial investigating the treatment of CCA with the combination of silmitasertib plus gemcitabine and cisplatin in comparison with gemcitabine and cisplatin found a statistically significant difference.
According to Senhwa Biosciences, the study’s findings indicate a clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) (P

The FDA has granted accelerated approval to pemigatinib (Pemazyre, Incyte Corporation) as the first treatment for adults with certain types of previously treated, advanced cholangiocarcinoma.
Ivosidenib improved progression-free survival with a promising trend toward improved overall survival in patients with IDH1-mutated cholangiocarcinoma.