
Top recent news in cancer drug development.
Chemosensitivity, treatment variations, and socioeconomic factors may be a significant factor.

Defective DNA repair mechanisms may contribute to Alzheimer's disease.

Researchers confirm antidepressants do not cause recurrence in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen.
Experimental personalized peptide cancer vaccine found to extend overall survival.

Top recent news in cancer drug development.
Portrazza plus chemotherapy treats metastatic squamous non-small cell lung cancer in patients who were not previously treated specifically for advanced lung cancer.
Increasing colon cancer awareness could exponentially decrease disease-related deaths.
Opdivo found to improve overall survival compared with other leading cancer therapies.
Tafinlar plus Mekinist found to improve overall survival in unresectable or metastatic BRAF-mutated melanoma.

Latest news in cancer drug development.

Study suggests increasing oxidative stress through with pro-oxidants may prevent metastasis.
Treatment helps reduce infection risk from low white blood cell count in cancer patients receiving chemotherapy.
Novel drug shows promise in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma refractory or resistant to current chemotherapies.

FDA requests a more thorough review of rociletinib from ongoing trial.
Opdivo shows extended overall survival and fewer adverse events in patients with RCC compared with Afinitor.
Patients with a family history of Lynch syndrome should be presented the option of risk prediction modeling.
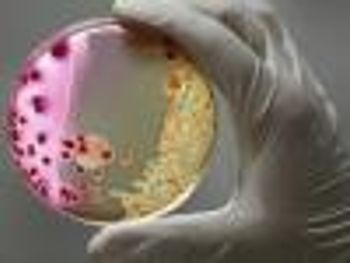
Clostridium sporogenes bacteria able to eradicate colon cancer tumor cells.
Top news of the week in cancer drug development.
Osimertinib (Tagrisso) is a once daily tablet for patients with metastatic epidermal growth factor receptor T790M mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer.
Hormone treatment may prove to be effective alternative option for patients with invasive lobular carcinoma.
Patients with cancer see a decline in employment, hours worked, individual income, and total family income following diagnosis.
Combination of Cotellic and Zelboraf shows superior overall and progression free survival in melanoma treatment.

Newly discovered pathway may prove effective target for treatment of triple-negative breast cancer.
Micro RNA based blood test may be used with imaging features to accurately predict disease severity.
Benefits of Plavix found to outweigh potential adverse events.
Recent news in cancer drug development.
People living in poorer areas less likely to receive screening.

Terms like revolutionary or miracle cause confusion for readers.
Intensity modulated radiation therapy shows less intense lung toxicity for more tolerable chemotherapy.